Vendor Privileged Access Management (VPAM)
What is Vendor Privileged Access Management?
Vendor Privileged Access Management, aka Vendor Access Management, is a tool that provides least privilege access for vendor employees, while also keeping track of what each of those individuals does with that access. More specifically, it's an implementation of Privileged Access Management (PAM) that helps organizations protect their digital infrastructure by managing and monitoring account access for third-party vendors.
This type of access control helps protect organizations from malicious actors or accidental data leaks.
A vendor is any individual or company with which an organization has an agreement to provide goods or services. These accounts are typically high-level accounts that have direct access to the organization’s most confidential information, such as financial records, customer data, personnel files, etc.
Companies often work with outside experts, consultants, and other third-party vendors who need privileged access to corporate resources. Companies engage with third-party vendors in different ways, such as a remote contractor working on a time-limited project, an embedded contractor, or outsourced staff augmentation.
What does Vendor Privileged Access Management do?
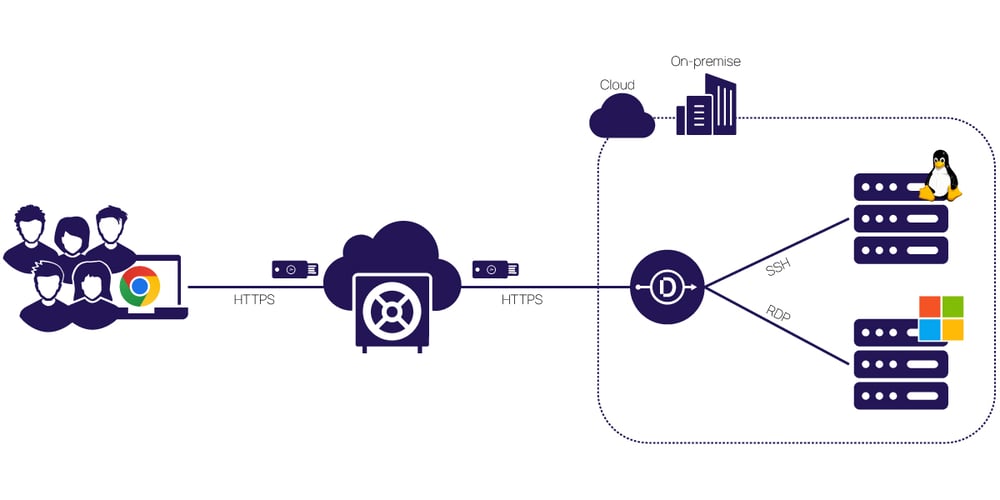
VPAM's primary purpose is to control and monitor privileged access provided to third parties, such as contractors, service providers, partners, etc. This includes providing temporary access for specific tasks or ongoing access for long-term projects.
With VPAM, companies can set up detailed policies on who can have privileged access and what type of privilege they have once they are granted access. This allows the company to maintain full control over access to sensitive information and data.
Another important feature of VPAM is its ability to detect suspicious behavior from vendors with privileged access in near real time. By monitoring user activity on a near continuous basis, VPAM can identify any unusual patterns or behaviors that might indicate malicious activity. It then alerts the organization so that it can take appropriate action as quickly as possible before a breach occurs.
How does Vendor Privileged Access Management function?
VPAM works by establishing a set of granular policies for each vendor account on the network. These policies determine what kind of resources each vendor can access and how they can interact with those resources. For example, a policy could be established that limits a vendor’s ability to modify certain files or directories within the system while still allowing them read-only access.
Additionally, each policy should include provisions for monitoring user activities and logging suspicious behavior in order to detect potential threats early on.

Need a step-by-step guide for planning your strategic journey to privileged access security?
Benefits of using Vendor Privileged Access Management
The main benefit of using VPAM is improved security for digital assets since it provides an extra layer of protection against malicious actors attempting to gain unauthorized entry into systems and applications. It also helps organizations ensure compliance with industry standards regarding data security while freeing up internal resources by streamlining the process of granting vendor privileges while reducing the manual effort required for monitoring activities.
Finally, using Vendor Privileged Access Management reduces the risk of insider threats because vendors only have access to the minimum amount of resources needed for their work, reducing the chances they will misuse those privileges or cause unintentional damage due to a lack of proper training or oversight.
How VPAM contains and mitigates the risks associated with third-party access
- Workflow tools: Automated workflows are used to manage vendor requests for privileged access rights. This ensures that all requests are handled in an efficient and secure manner while ensuring compliance with regulations such as GDPR or HIPAA.
Imagine the lifecycle of a vendor’s access: Authorize, Provision, Retain / Reclassify, Decommission, and at the end of the cycle, the account could be renewed, re-approved, disabled, or expired. With PAM, you can create a standard, automated workflow to be used whenever a third party needs access to specific resources.
By automating the workflow, you ensure that all contractors and vendors provide any requisite information, confirm that they are aware of acceptable use policies (and have signed off on them), and also receive management approval to grant them privileged access. All of this could be done in a central portal to keep track of all vendors and systems, even if they don’t have a company-issued computer or email address. - Policy-based roles and least privilege access: The first step when granting access is to ensure the vendor is given an appropriate level of access and no more. You can use role-based access control (RBAC) to configure baseline and default access. This defines which systems the vendor can access and their rights within each system. You can place a time limit on each account, automatically revoking access unless it is reviewed and extended.
- Monitoring: With advanced PAM, you can track each vendor’s privileged account activity, including which systems they access and actions taken within those systems. Depending on their level of privileged access, the sensitivity of their work, and the overall risk profile of the engagement, consider using tools for session monitoring, session recording, and keystroke logging.
- Anomalous behavior detection: In conjunction with session monitoring, you can enable anomalous behavior detection. Is the vendor accessing systems to which they should not have access? Is there a sudden increase in account access by certain users or systems? Is there atypical access to certain privileged accounts? Are accounts accessed at odd times of the day or from unexpected locations? Automated monitoring coupled with behavioral analytics helps identify risks to privileged accounts so you can take appropriate action.
- Discovery: You can use privileged account discovery tools to periodically check for unused or unknown accounts and make sure they are included in your central portal. Only current third-party vendors in good standing should retain access.
Secure privileged remote access for everyone