Streamlining compliance: The power of broad cybersecurity frameworks
Data breaches and cyber threats have become increasingly pervasive in today's rapidly evolving digital landscape. To safeguard sensitive information and maintain trust, we are bombarded with security regulations and laws.
What's the compliance conundrum?
Large organizations across industries must grapple with dozens of security regulations and laws, each with requirements, controls, and reporting mechanisms. From GDPR and HIPAA to PCI DSS and SOX, the compliance landscape can feel like a labyrinth. Navigating this complex regulatory landscape can be daunting, consuming valuable resources and time.
Treating each regulation individually is an arduous endeavor that demands significant effort, expertise, and resources. Moreover, the risk of overlooking critical compliance gaps is ever-present when dealing with so many regulations, often annually.
However, there's a beacon of hope that can help you efficiently manage your compliance efforts.
The power of broad cybersecurity compliance frameworks
Enter a solution: broad compliance frameworks. While standards offer specific guidelines and methods, regulatory compliance frameworks provide a more general approach and best practices for implementing a successful cybersecurity program. Various organizations, including government agencies, industry associations, standards bodies, and independent research institutions, develop regulatory cybersecurity compliance frameworks. They provide a structured approach to managing cybersecurity risk while addressing compliance requirements.
You can use several widely recognized cybersecurity compliance frameworks to establish and improve your cybersecurity practices. These frameworks provide structured guidelines and best practices for managing cybersecurity risks.
Below is a sampling of popular compliance frameworks:
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF): Developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), this framework offers a comprehensive approach to managing cybersecurity risks. It focuses on five core functions: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover (and soon with version 2.0 – Govern.)
Whitepaper: Meet NIST SP 800-171 Requirements with Delinea - PCI DSS: The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard mandates businesses handling credit card transactions to maintain a secure environment for cardholder data protection, fraud prevention, and data breach avoidance. It covers secure networks, data encryption, vulnerability management, access control, monitoring, and policies.
Whitepaper: Delinea PAM helps you align with PCI DSS Requirements - HITRUST Common Security Framework (CSF) is a widely used security framework for the healthcare sector. It offers controls and best practices to manage risks and protect sensitive healthcare data, aligning with regulations and industry standards. The framework safeguards the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive healthcare data, all while ensuring compliance with necessary regulations.
- CIS Critical Security Controls (formerly known as the SANS Top 20): The Center for Internet Security (CIS) offers a list of 20 critical security controls that organizations can implement to improve their cybersecurity posture. These controls prioritize the most common and impactful threats. Unlike the NIST CSF, it focuses on lowering risk and boosting resilience, omitting risk analysis and management.
Whitepaper: Mapping Delinea PAM to CIS Critical Security Controls - COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies): COBIT is a framework developed by ISACA that focuses on aligning IT governance and control practices with business objectives. It provides comprehensive controls and guidelines for managing and governing information and technology resources.
- FFIEC Cybersecurity Assessment Tool: The Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council (FFIEC) provides a framework to help financial institutions assess their cybersecurity risk and develop appropriate risk management strategies.
- MITRE ATT&CK Framework: This framework focuses on adversary behavior and tactics. It provides a comprehensive model of real-world attacker techniques, tactics, and procedures (TTPs) to help organizations understand and defend against cyber threats.
eBook: Conversational MITRE ATT&CK Framework
Note that some of these can be considered both a standard and a framework depending on context. For example, HITRUST is a framework that includes, harmonizes, and cross-references existing, globally recognized standards, regulations, and business requirements, including ISO, NIST, PCI DSS, and HIPAA.
As you can see, these compliance frameworks offer guidelines for various industries and contexts. It's important to note there is no one-size-fits-all, and some compliance frameworks may overlap in certain areas. Choose a framework based on your organizational and regulatory needs. Do you prioritize improving compliance? Reducing costs? Beefing up your incident response processes?
How do you implement a compliance framework in your organization?
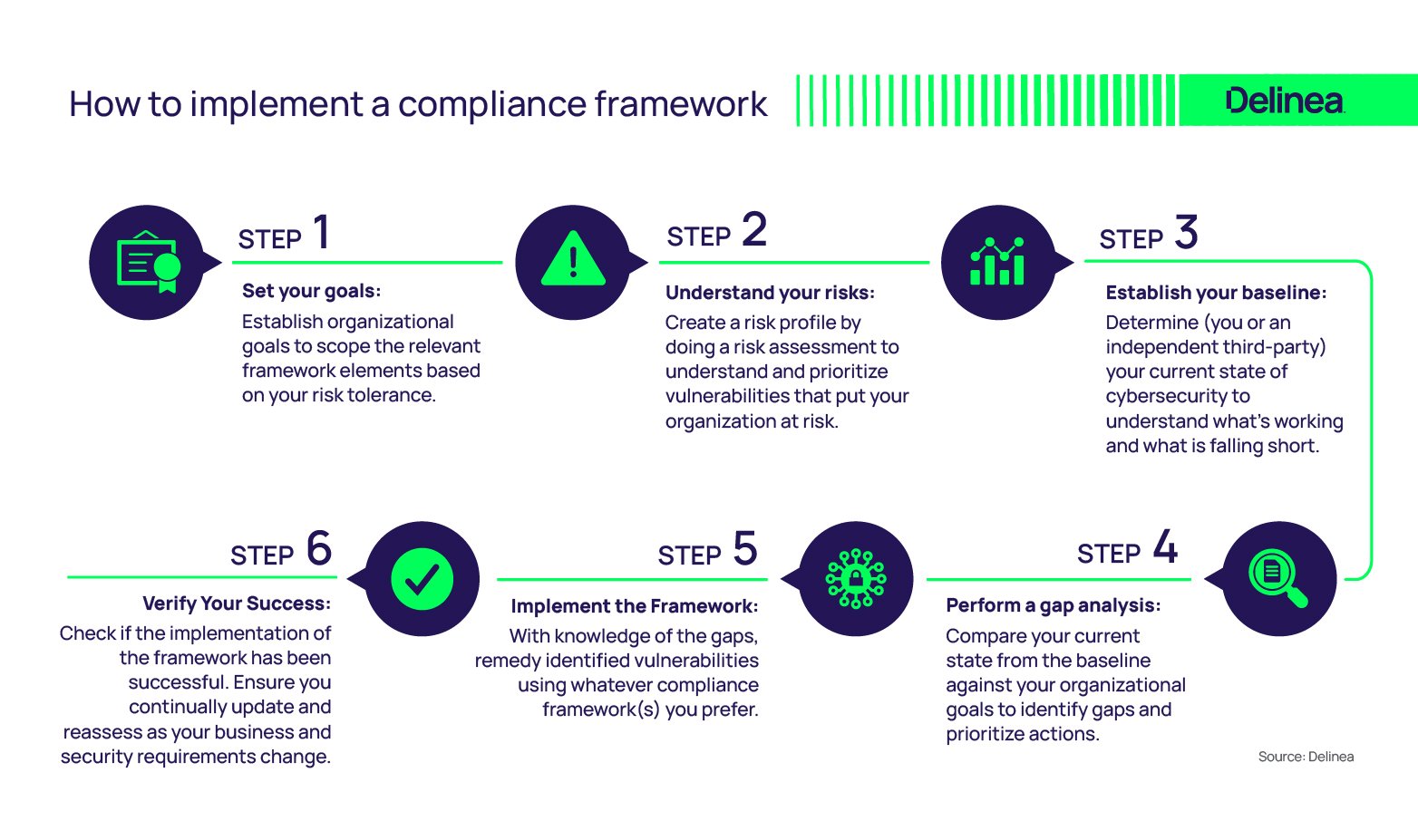
Most frameworks provide self-help tools. For example, the NIST CSF Quick Start Guide. They tend to focus on step 5, below, implementing their framework. However, here is a broader set of generic guidelines:
![]() Set your goals:
Set your goals:
Establish organizational goals to scope the relevant framework elements based on your risk tolerance.
![]() Understand your risks:
Understand your risks:
Create a risk profile by doing a risk assessment to understand and prioritize vulnerabilities that put your organization at risk.
![]() Establish your baseline:
Establish your baseline:
Determine (you or an independent third party) your current state of cybersecurity to understand what's working and what is falling short.
![]() Perform a gap analysis:
Perform a gap analysis:
Compare your current state from the baseline against your organizational goals to identify gaps and prioritize actions.
![]() Implement the Framework:
Implement the Framework:
With knowledge of the gaps, remedy identified vulnerabilities using whatever compliance framework(s) you prefer.
![]() Verify Your Success:
Verify Your Success:
Check if the implementation of the framework has been successful. Ensure you continually update and reassess as your business and security requirements change.
Is there a ripple effect of compliance framework adoption?
Adopting a broad regulatory compliance framework and aligning its recommendations to your organization's security measures lays the foundation for a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy. It can help you comply with other regulations by providing a common language and principles for cyber that unifies the conversation around cyber risk and security. The beauty of embracing a cybersecurity compliance framework such as the NIST CSF is its ripple effect on your organization's compliance efforts.
The NIST based its Framework on existing standards, guidelines, and practices. By applying its outcomes that address cybersecurity risk, you inadvertently address a substantial portion of requirements from the regulations and laws you must comply with. This consolidation of efforts significantly reduces the burden of treating each regulation individually.
For instance, if you comply with the NIST CSF's data protection, access controls, and incident response guidelines, you'll likely have covered many GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS requirements. That effort saves time and ensures a more consistent and robust security posture across your organization.
In addition, compliance frameworks such as NIST CSF are living documents regularly updated, so you can use them to stay up-to-date on cybersecurity changes, trends, and requirements. Also, addressing global needs is a critical part of NIST's work in the evolution of the CSF, especially as it continues to see international adoptions and use cases to address emerging risks. The Framework is now available in more than ten languages.
What are some examples of how such a compliance framework applies to me?
- The NIST SP 800-171 references the broader security framework of NIST CSF, aligning with the CSF's core functions and categories to ensure a consistent approach to cybersecurity and risk management.
- The ISO/IEC 27001 standard is often used as a benchmark for compliance with industry regulations, such as the European Union's GDPR.
- While HIPAA itself is a comprehensive regulation, it references the broader security framework of the NIST SP 800-53, "Security and Privacy Controls for Federal Information Systems and Organizations." NIST SP 800-53 provides a comprehensive catalog of security controls and guidelines applicable to Federal information systems, and it serves as a valuable resource for organizations seeking to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of ePHI while aligning with HIPAA's requirements.
- The CIS Critical Security Controls are designed to be implemented by organizations of all sizes and industries. They often supplement other cybersecurity frameworks, such as the NIST CSF and the ISO/IEC 27001 standard.
- The Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) provides guidelines and regulations for financial institutions in Singapore, including banks, insurance companies, and other financial services providers. One of its fundamental guidelines is the Technology Risk Management (TRM) guidelines, which outline the requirements for managing technology and cybersecurity risks in the financial sector.
They reference broader security frameworks, such as the ISO 27001 and the NIST CSF. By referencing these frameworks, the MAS aims to provide financial institutions with a comprehensive and practical approach to managing technology and cybersecurity risks in line with global standards.
Do such compliance frameworks address all requirements?
While broad cybersecurity regulatory compliance frameworks offer a comprehensive approach and build upon the same foundational principles, some regulations may have specific requirements not explicitly covered by the framework. However, with most of the security landscape already addressed through the implementation of the compliance framework, your organization can focus on identifying and addressing the gaps unique to individual regulations. This targeted approach allows for a more streamlined and efficient compliance process.
Some compliance frameworks focus exclusively on security, while others focus on privacy. Security and privacy have many commonalities, so you should consider adopting both. For example, NIST CSF plus the NIST Privacy Framework. You may already have an Enterprise Risk Management program integrating all your risk management efforts, including security and privacy.
Embrace, implement, and excel!
In an era where cybersecurity threats are constantly present and compliance requirements continue to evolve, organizations must seek innovative strategies to manage and streamline their security efforts effectively. Adopting broad cybersecurity compliance frameworks like the NIST CSF offers a beacon of light in the often-convoluted compliance landscape. By embracing and implementing the recommended security measures, organizations can experience the dual benefits of enhanced cybersecurity and a more efficient compliance process.
These regulatory compliance frameworks provide a roadmap that helps you navigate the intricate maze of regulations while ensuring your security practices remain robust. The result? A strengthened security posture, reduced compliance-related stress, and the ability to focus resources on addressing the unique aspects of each regulation. It's a win-win strategy that will empower you to excel in cybersecurity while maintaining compliance with less friction.

WHITEPAPER
Simplify your compliance journey


