Key highlights from the 2023 Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report
It’s that time of year again. The 2023 Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report is out, and it’s packed with the latest information on frequency, vectors, and impact of cyberattacks.
Stolen Credentials are the top way for cybercriminals to get into organizations.
While the good folks at Verizon make the report lighthearted and always fun to read, there’s no way around it: the contents are both positive and disturbing. Reading the entire report can be overwhelming, when you consider the staggering losses, diversity of emerging threats, and growing number of cyber strategies it implies you should enforce to prevent and contain cyber incidents and breaches.
That’s why, in this blog, we’re highlighting the most likely attacks, the most impactful consequences, and the most beneficial security controls you can implement, based on the findings of VDBIR.
What is the Verizon DBIR?
The Verizon DBIR analyzes thousands of cybersecurity incidents, breaks them down into categories, and turns all the data into something actionable. This helps us realign our best practices and make the digital world a safer place. It is an important annual report for security professionals—it's like our industry scorecard on what's changed, how the attackers are doing, and what we're doing better.
This year is the 16th Verizon DBIR, and it covers 81 countries, 16,312 incidents, and 5,199 data breaches, showing that cybercriminals continue to target organizations for financial gain. Organized cybercrime continues to be on the rise, meaning that the cyber defenders tasked with protecting organizations must remain vigilant and ready to respond at any moment.
What’s the difference between an incident vs. a breach?
While incidents and data breaches are related to one another, in cybersecurity terms they are different.
What is an incident:
An incident refers to any event or occurrence that could potentially compromise the security, integrity, or availability of computer systems, networks, or data. It encompasses a broad range of events, including unauthorized access attempts, malware infections, system malfunctions, physical security breaches, policy violations, and more. Incidents can be intentional (such as cyberattacks) or unintentional (such as accidental data deletion).
What is a data breach:
A data breach specifically refers to an incident where sensitive, confidential, or protected information is accessed, disclosed, or stolen by an unauthorized individual or entity. In a data breach, the security measures protecting the data have been circumvented or compromised, resulting in unauthorized access to the data. Data breaches can involve various types of data, such as personally identifiable information (PII), financial records, intellectual property, or trade secrets.
Which cybersecurity frameworks are used in the Verizon DBIR?
Now let’s take a look at the cybersecurity frameworks used in the Verizon DBIR.
VERIS Framework
The VERIS (Vocabulary for Event Recording and Incident Sharing) framework is a standardized framework developed by the Verizon Business Risk Team to provide a common language and structure for describing security incidents. It aims to enhance the sharing and analysis of incident data among organizations, allowing for better understanding, comparison, and mitigation of security incidents.
By systematically categorizing incidents using the VERIS framework, organizations can gain insights into the nature and impact of security incidents, benchmark their incident response capabilities, and share anonymized incident data with others to improve collective knowledge and defenses against cybersecurity threats.
MITRE ATT&CK Framework
The MITRE ATT&CK framework is a comprehensive knowledge base that provides a structured and globally accessible repository of tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) used by adversaries during cyberattacks. It is designed to help organizations understand, detect, and respond to advanced cyber threats more effectively.
Check out my colleague Tony Goulding’s recent blog that goes into in-depth details on the MITRE ATT&ACK framework: Unlocking Cybersecurity Insights: Exploring the MITRE ATT&CK Framework
Center for Internet Security Controls
The CIS Controls, also known as the Center for Internet Security Controls, is a set of cybersecurity best practices and guidelines that organizations can implement to improve their overall security posture. These controls are widely recognized as an effective framework for managing and mitigating cyber threats.
So, what are the key insights, best practices, and risk reduction recommendations from this year’s report? With so many different threats to deal with, I have focused on those that impact everyone and the ones that have a significant effect on businesses.
Here are my top key takeaways from this year’s Verizon DBIR:
Key Takeaway 1: Stolen Credentials are the top technique used to gain unauthorized access
Stolen credentials are popular with attackers because they provide a direct and relatively easy path to gaining unauthorized access.
Attackers can use stolen credentials to masquerade as legitimate users, bypass security measures, and access sensitive data. Stolen credentials often come with elevated privileges, allowing attackers to move laterally within a network and escalate their control. Stolen credentials are commonly used in multi-step attacks such as ransomware and Basic Web Application attacks, in which 86% of these attacks involved the use of stolen credentials.
To reduce the risks associated with stolen credentials, organizations should implement strong password policies, enforce Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), follow the principle of least privilege, monitor credentials for unusual activity, provide user education and awareness, regularly rotate credentials, and securely store credentials in a Privileged Access Management (PAM) solution. By implementing these practices, organizations can mitigate the risk of unauthorized access through stolen credentials and improve their overall security posture.
Key takeaway 2: Business Email Compromise is on the rise as the fastest way to make money
Business Email Compromise (BEC) is a type of cyberattack where attackers use social engineering tactics to compromise business email accounts and deceive employees into performing fraudulent actions or sharing sensitive information.
To reduce the risks of BEC attacks, organizations can implement various measures:
- Conducting security awareness training to educate employees about BEC and phishing techniques
- Implementing strong email authentication protocols
- Enabling Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for email accounts
- Monitoring email accounts for suspicious activity
- Establishing secure payment processes
- Verifying communications through out-of-band channels
- Deploying email filtering and anti-spam solutions
- Conducting vendor due diligence
- Developing an incident response plan
- Staying updated on the latest BEC attack techniques
By implementing these strategies, organizations can enhance their defenses and mitigate the risks associated with BEC attacks.
Social engineering using pretexting is on the rise
Social engineering using pretexting is a deceptive technique where attackers create a false scenario or identity to trick individuals into divulging sensitive information or performing actions they wouldn't typically do.
The attacker impersonates a trusted person or authority figure, establishes credibility, and exploits the target's trust. They gather information and construct a convincing pretext, often using psychological manipulation. Once the target's trust is gained, the attacker extracts confidential data or gains unauthorized access.

To mitigate risks, individuals and organizations should be skeptical of unsolicited requests, independently verify identities, limit sharing of personal information, implement security policies and training, and practice least privilege. By staying vigilant and cautious, individuals and organizations can protect themselves against pretexting attacks.
Key Takeaway 3: Ransomware is holding steady but still a huge threat to the world
Ransomware is considered a top threat due to its significant impact on individuals, organizations, and even critical infrastructure. It’s a type of malicious software that encrypts files or locks computer systems, demanding a ransom payment in exchange for restoring access.
To reduce the risks associated with ransomware, organizations and individuals can take several steps:
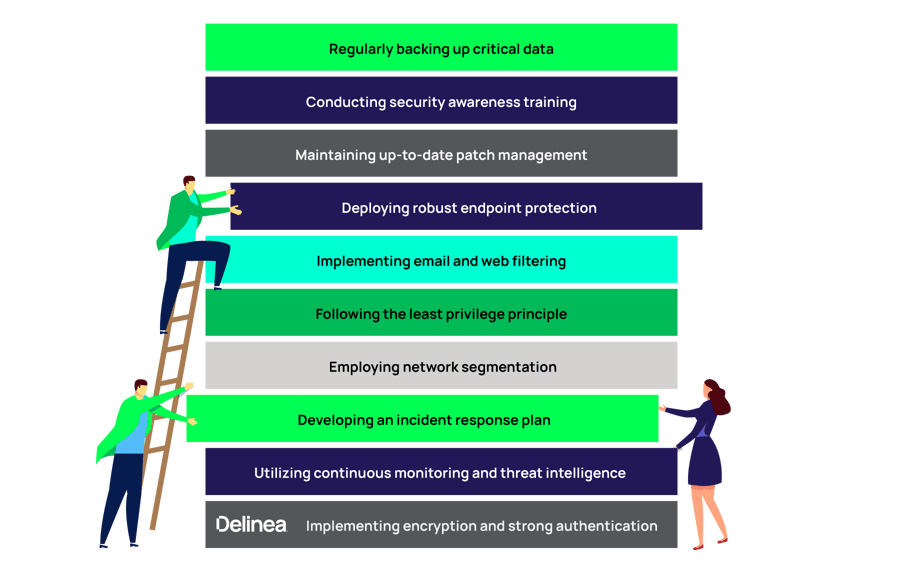
By implementing these measures, individuals and organizations can enhance their defenses and reduce the likelihood of falling victim to ransomware.
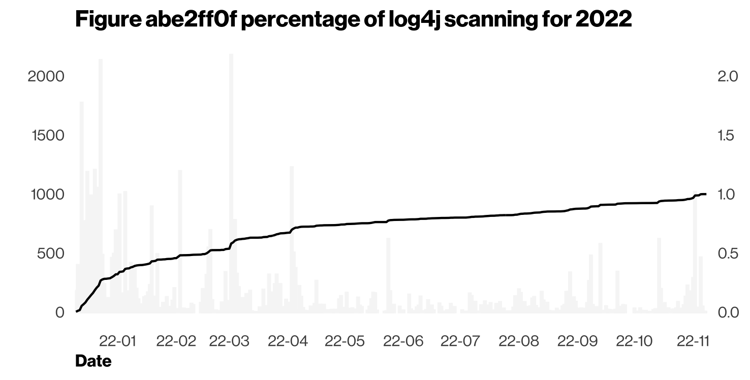
Log4J was 2022’s top vulnerability
A few other notable references in this year’s report included the Log4J vulnerability, which was one of the most exploited vulnerabilities. The Log4J vulnerability was most abused within the first 30 days. The security industry responded quickly, with patches mitigating what could have been potentially catastrophic for many businesses. The good news is that the vulnerability was quickly addressed.
Percentage of Log4j scanning in 2022
More than 32% of all Log4j scanning activity over the course of the year happened within 30 days of its release
Source: Verizon 2023 Data Breach Investigations Report
PAM use cases in the Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report (and what you should do about them)
So many roads in the Verizon DBIR lead to Privileged Access Management. No surprise there, as PAM has been widely cited by Gartner Research and other analyst organizations for several years as the #1 cybersecurity strategy to implement.
PAM includes critical cybersecurity strategies such as:

A unified PAM solution can address all these use cases with a common user experience and modular components. As you consider strategies to combat the top challenges raised in the Verizon DBIR, you don’t have to hunt for multiple, specialized standalone solutions and struggle to make them work together. With an enterprise-scale PAM solution, you can address them all.
Stolen credentials
According to the Verizon report, the use of stolen credentials is the top action cybercriminals take to achieve their goals, even topping ransomware. When accessing organizations, 44.7% of cyber attackers use stolen credentials, an increase from last year’s 41.7%. With those stolen credentials, criminals compromise all types of data, most commonly personal data (73%) and medical data (34%).
There are several ways PAM prevents valuable credentials from being stolen. As the most basic level, PAM solutions include an encrypted vault for all types of credentials, including passwords, secrets, and SSH keys. Users must “check out” a credential from the vault to use it to access critical and sensitive systems and data.
With PAM, credentials such as complex passwords are created behind the scenes and most users never know what they are. This reduces the risk of sharing credentials, putting them in places where they can be easily stolen (like Post-It notes or spreadsheets), and creating passwords that are easy to guess.
Plus, PAM provides additional checks to ensure that the person using a credential is who they say they are. Controls such as Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) authenticate identities that are associated with credentials. So, even if a credential is stolen, a user will be blocked from using it.
Privilege misuse
VDBIR reports that nearly half (49%) of incidents involve privilege misuse, meaning people are “using privileges for any purpose or manner other than that for which was intended.”
This often happens when a user is granted blanket privileges, allowing them broad access to systems, rather than granular access based on their role and responsibilities. Such practices violate least privilege, zero trust best practices, and break compliance requirements. It can also happen when it’s easy to share privileges with others.
PAM solutions help you uphold those best practices and ensure access only to what people need and when they need it, thanks to granular access control policies With oversight such as session monitoring, immutable audit trails, and privileged behavior analytics, you can make sure that privileges aren’t being misused.
Endpoint breaches
Servers are the primary asset impacted by data breaches. They are a casualty of over 80% of successful attacks. According to the report, servers are “common targets in almost all of the attack patterns, but especially in our System Intrusion, Basic Web Application Attacks, Miscellaneous Errors and Denial of Service patterns.”
PAM prevents and contains server-based attacks by controlling privileged access at the server level. Instead of standing privileges, people and service accounts that need access to servers can rely on Just-in-Time (JIT) privileged elevation to gain access for a limited time, for limited capabilities. Under those conditions, a cyber attacker who gains access to a single server would be unable to cause damage by escalating privileges and navigating from server to server, causing damage.
User devices, including workstations, were impacted in nearly 20% of the cases included in the report.
Again, PAM has a solution. PAM prevents and contains workstation-based attacks by removing the need for local admin rights on most users’ machines, a rich target for cybercriminals. Instead, employees can rely on application control policies to conduct necessary activities, and access approved applications. Then, even if a cyber attacker gains access to a user workstation, their privileges will be limited, and the attack will be contained.
Secure remote connections
Desktop sharing software, commonly used for remote troubleshooting, is also a frequent attack vector for ransomware, says Verizon, as it allows criminals to gain access to a system.
Rather than rely on risky software for remote sharing, PAM capabilities like remote access control and session management allow you to make secure remote connections using a variety of protocols.
MITRE ATT&CK path and privilege escalation
One of the unique aspects of the 2023 Verizon report is the discussion on working with the MITRE ATT&CK and the CIS Critical Security Controls to assist organizations with developing and maintaining a data-driven cybersecurity program. Verizon says they have mapped their methodology to ATT&CK to make it more “real world.”
As they explain, a key aspect of ATT&CK is the idea that “once attackers have access to your environment, they will typically look for ways to escalate privileges, maintain persistence and locate paths to move across the organization to achieve their ultimate goal, whatever that may be.”
It’s important to note that attacks aren’t always linear. They can head down a path—perhaps from workstation to server—then to server 2, databases, cloud platforms, and back.
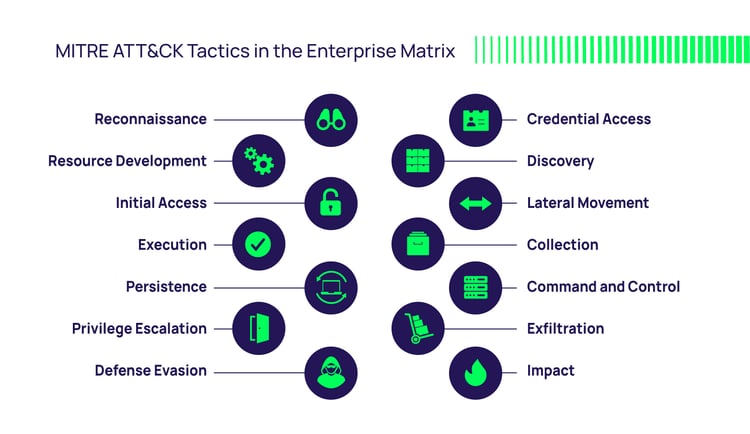
Above: Tactics described by the MITRE ATT&CK Enterprise Matrix Framework
For that reason, PAM controls for privileged access and privilege elevation should extend throughout your organization, especially as it becomes more diverse and complex. Then, attacks can be detected quickly and shut down before they cause real damage.
What does cybersecurity like this cost? Not as much as you think