Uncovering the risks of unmanaged identities
Unmanaged identities pose significant risks to your organization's security, compliance, and business operations. So, what's the best way to continuously uncover and secure them?
Unmanaged identities defined
Unmanaged identities are those that are not tracked, governed, or protected by identity management systems in any way. This can happen unintentionally or can occur when gaps in your normal identity or security processes leave an identity stranded.
Unmanaged identities can be both human and non-human identities (NHIs). Here are the major identity types, as well as warnings on how leaving them unmanaged can present non-negotiable risks for your organization. Included are additional blog reading on each type if you’re interested:
- IT admins: Unmanaged IT admin identities can lead to excessive permissions and the creation of backdoor accounts, increasing the risk of unauthorized access and potential damage. Shared privileged accounts make it difficult to track individual actions, especially when IT operations are outsourced, leading to oversight challenges.
Securing IT admin, workforce, machine, and developer identities
- Workforce users: Workforce identities are vulnerable to human error, which is a top breach vector. The rise in remote work increases exposure to identity-based attacks, making them prime targets for ransomware. Orphaned accounts and privilege creep can lead to unauthorized access and fraud.
Securing workforce identities: Strengthening the identity chain - Developers: Developers often require access to critical systems and data, which can lead to security risks if not properly managed. They may include remote third parties or short-term hires, increasing the risk of unmanaged access. Developers need fast access, which can lead to bypassing security protocols.
Securing IT admin, workforce, machine, and developer identities - Machine & AI: Machine identities, including AI agents, are proliferating due to automation and AI workflows. These identities can be compromised, leading to unauthorized access to automated systems and sensitive data. AI poisoning and the rise of Agentic AI expand the attack surface, posing significant risks if compromised.
Securing machine and AI identities: Risks, challenges, and solutions
This last category of machine and AI identities is gaining a lot of attention as organizations build out and deploy their AI systems and need to actively secure these elements.
The unique challenge of managing Agentic AI identities
Agentic agents are part of an AI system capable of making decisions, interacting with other agents, and completing tasks independently.
- Unmanaged agentic AI agents often operate independently, making it difficult to track and monitor their activities without a centralized management system.
- These AI agents can adapt and change their behavior autonomously, which complicates efforts to predict and control their actions.
- While performing their duties, AI agents can spin up other models and agents that have access to valuable data.
- They can exist across various platforms and environments, including cloud, on-premises, and hybrid systems, leading to fragmented visibility.
The ease of deploying and scaling AI agents has led to rapid proliferation, outpacing traditional management and oversight capabilities.
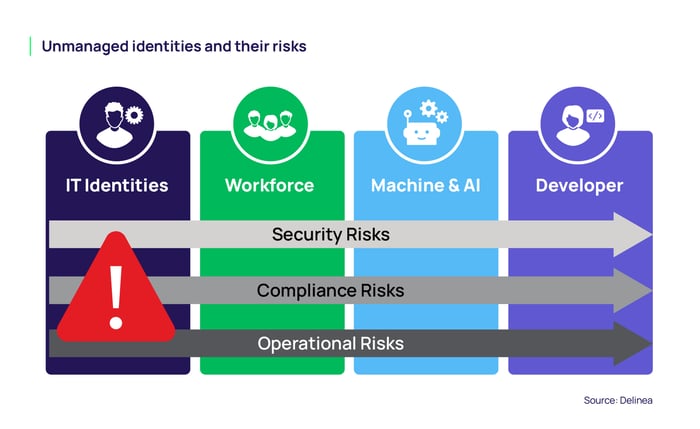
The risks associated with unmanaged identities
The risks are manifold and can be broken down into three broad categories:
Security risks:
Unmanaged identities significantly expand the attack surface, providing more entry points for attackers. They are prime targets for credential theft, which can lead to lateral movement within an organization's network. Forgotten or over-permissioned accounts can facilitate privilege escalation, allowing attackers to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data. Real-world breaches have been linked to unmanaged identities, underscoring the critical need for effective identity management.
Compliance and regulatory risks:
Organizations are required to meet various compliance standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, and SOX. Unmanaged identities can lead to failures in meeting these requirements, resulting in audit challenges due to incomplete identity inventories. The potential for fines and reputational damage is significant if unmanaged identities lead to data breaches or non-compliance.
Operational risks:
Inefficient access management due to unmanaged identities increases IT overhead and complexity. Unauthorized access or accidental deletions can disrupt business operations, leading to breaches, financial losses, and diminished customer trust.
Why are unmanaged identities so hard to control?
Several factors contribute to the difficulty in controlling unmanaged identities:
- Lack of centralized visibility:. Organizations often lack a unified view of identities across different environments.
- Siloed IT and security teams: Disconnected teams can lead to gaps in identity management.
- Rapid cloud adoption and DevOps practices: These can outpace traditional identity management processes.
- Inadequate offboarding processes: Failure to properly deprovision accounts when employees leave.
- Shadow IT and business-led technology adoption: These create identities outside the purview of IT departments.
Best practices for discovering and managing unmanaged identities
Organizational members, from the C-suite to IT, security, and identities teams on down, should be aware that a good percentage of their identities in their environment are unknown and therefore unmanaged. But modern forward-leaning identity solutions are helping to give visibility and control back. Here are some best practices to keep in mind:
- Continuous Identity Discovery and inventory: It's important to continuously discover new human and machine identities throughout your multi-cloud and on-premise environments.
- Automated provisioning and deprovisioning: Implement automated processes to manage the lifecycle of identities so that dormant or unused identities are disconnected.
- Least Privilege and just-in-time access: Limit access rights to all identities – not just human ones - to the minimum necessary and provide access only when needed.
- Regular audits and access reviews: Conduct periodic reviews to ensure compliance and identify anomalies.
- Leveraging identity governance and Privileged Access Management (PAM) solutions: Use advanced tools to manage and secure identities and select a vendor that understands how to find, manage and secure identities in all types of complex IT environments.
The role of modern identity security solutions
Modern identity security solutions such as Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management (CIEM), Privileged Access Management (PAM), and Identity Governance and Administration (IGA) play a crucial role in uncovering and remediating unmanaged identities. These tools provide organizations with the ability to reduce risk, improve compliance, and enhance operational efficiency by offering visibility and control over all identities.
Unmanaged identities present a clear danger to organizations. They increase the risk of security breaches, compliance failures, and operational disruptions. It is imperative for organizations to prioritize identity discovery and management as a core security practice.
In the age of digital transformation, visibility and control over all identities are non-negotiable. By implementing robust identity management practices and leveraging modern security solutions, organizations can safeguard their digital assets and ensure business continuity. Reach out to Delinea to discuss how we can help de-risk your identity sprawl and rein in your identities.


